Overview
-
Download the data we use in the workshop, and have an up-to-date web browser.
-
If you are attending this workshop remotely, please install/update the Zoom video conferencing application.
-
For this workshop, we are using a cloud instance of RStudio provided by LSIT that comes with all the necessary packages. If you choose this option, you will not need to install anything for the workshop. You only need to sign on with your UCSBnetID and upload the data.
-
If you would like to go through the workshop with your local RStudio instead, you may follow the below instructions, make sure to follow the instructions for setting up GDAL and the Spatial Extensions!
-
Make sure you can make the test map below by running the .r script that came along with the data files. If you cannot make this map appear in R, make sure you have the spatial components configured correctly and ask for help!
Data (Required)
You can download all of the data used in this workshop by clicking this download link. The file is 218.2 MB.
Clicking the download link will automatically download all of the files
to your default download directory as a single compressed (.zip) file.
To unzip this file, double click the folder icon in your file navigator
application (for Macs, this is the Finder application). Inside are 4 more
zip archives. Each of these 4 also need to be unzipped!
For a full description of the data used in this workshop see the data page.
If you are using our cloud LSIT RStudio, unzip the data folder and also unzip the four folders inside of it! Upload these four folders to your online RStudio.
Zoom Install and Update
Install the videoconferencing client
If you haven't used Zoom before, go to the official website to download and install the Zoom client for your computer.
Set up your workspace
Like other Carpentries workshops, you will be learning by "coding along" with the Instructors. To do this, you will need to have both the window for the tool you will be learning about (a terminal, RStudio, your web browser, etc..) and the window for the Zoom video conference client open. In order to see both at once, we recommend using one of the following set up options:
- Two monitors: If you have two monitors, plan to have the tool you are learning up on one monitor and the video conferencing software on the other.
- Two devices: If you don't have two monitors, do you have another device (tablet, smartphone) with a medium to large sized screen? If so, try using the smaller device as your video conference connection and your larger device (laptop or desktop) to follow along with the tool you will be learning about.
- Divide your screen: If you only have one device and one screen, practice having two windows (the video conference program and one of the tools you will be using at the workshop) open together. How can you best fit both on your screen? Will it work better for you to toggle between them using a keyboard shortcut? Try it out in advance to decide what will work best for you.
Software
You should already have R and R Studio
| Software | Install | Manual | Available for | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Link | Link | Linux, MacOS, Windows | Software environment for statistical and scientific computing |
| RStudio | Link | Linux, MacOS, Windows | GUI for R |
Please update your base R to at least 4.1.1!
We provide quick instructions below for installing the various software needed for this workshop. At points, they assume familiarity with the command line and with installation in general. As there are different operating systems and many different versions of operating systems and environments, these may not work on your computer. If an installation doesn’t work for you, please use our LSIT Cloud RStudio
R
Participants who do not already have R installed should download and install it.
Windows
To install
R, Windows users should select “Download R for Windows” from RStudio and CRAN’s cloud download page, which will automatically detect a CRAN mirror for you to use. Select thebasesubdirectory after choosing the Windows download page. A.exeexecutable file containing the necessary components of base R can be downloaded by clicking on “Download R 3.x.x for Windows”.
macOS
To install
R, macOS users should select “Download R for (Mac) OS X” from RStudio and CRAN’s cloud download page, which will automatically detect a CRAN mirror for you to use. A.pkgfile containing the necessary components of base R can be downloaded by clicking on the first available link (this will be the most recent), which will readR-3.x.x.pkg.
Linux
To install
R, Linux users should select “Download R for Linux” from RStudio and CRAN’s cloud download page, which will automatically detect a CRAN mirror for you to use. Instructions for a number of different Linux operating systems are available.
RStudio
RStudio is a GUI for using R that is available for Windows, macOS, and various Linux operating systems. It can be downloaded here. You will need the free Desktop version for your computer. In order to address issues with ggplot2, learners and instructors should run a recent version of RStudio (v1.2 or greater).
GDAL and the Spatial Extensions
The installation of the geospatial libraries GDAL, GEOS, and PROJ.4
varies significantly based on operating system. These are all
dependencies for sf, the R package that we will be using for spatial
data operations throughout this workshop.
Mac users beware!
Windows
To install the geospatial libraries, install the latest version RTools
macOS - Install with Packages (Beginner)
If you have installed software such as QGIS or GRASS, you may already have most of these dependancies taken care of.
You may or may not need to install various underlying components of GDAL. You can get everything necessary for the workshop (GDAL, GEOS, PROJ) in one package by installing the latest version of Kyng Chaos’s pre-built package for GDAL Complete. Be aware that several other libraries are also installed, including the UnixImageIO, SQLite3, and
NumPy. Please install all items in the package.After downloading the package in the link above, you will need to double-click the cardbord box icon to complete the installation. Depending on your security settings, you may get a warning message about “unidentified developers”, but you may continue with the installation. Please contact us or attend the workshop install party if you need help enabling the installation.
macOS - Install with Homebrew (Advanced)
Alternatively, participants who are comfortable with the command line can install the geospatial libraries individually using homebrew. We do not have the expertise to provide assistance on your installation using this method.
$ brew tap osgeo/osgeo4mac && brew tap --repair $ brew install proj $ brew install geos $ brew install gdal2
Linux
Steps for installing the geospatial libraries will vary based on which form of Linux you are using. These instructions are adapted from the
sfpackage’sREADME.For Ubuntu:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntugis $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install libgdal-dev libgeos-dev libproj-devFor Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install gdal-devel proj-devel proj-epsg proj-nad geos-develFor Arch:
$ pacman -S gdal proj geosFor Debian: The rocker geospatial Dockerfiles may be helpful. Ubuntu Dockerfiles are found here. These may be helpful to get an idea of the commands needed to install the necessary dependencies.
UDUNITS
Linux users will have to install UDUNITS separately. Like the geospatial libraries discussed above, this is a dependency for the R package sf. Due to conflicts, it does not install properly on Linux machines when installed as part of the sf installation process. It is therefore necessary to install it using the command line ahead of time.
Linux
Steps for installing the geospatial will vary based on which form of Linux you are using. These instructions are adapted from the
sfpackage’sREADME.For Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt-get install libudunits2-devFor Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install udunits2-develFor Arch:
$ pacaur/yaourt/whatever -S udunitsFor Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install -y libudunits2-dev
R Packages
The following R packages are used in the various geospatial lessons.
To install these packages in RStudio, do the following:
1. Open RStudio by double-clicking the RStudio application icon. You should see
something like this:
2. Type the following into the console and hit enter.
install.packages(c("dplyr", "ggplot2", "raster", "rgdal", "rasterVis", "sf"))
You should see a status message starting with:
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/macosx/el-capitan/contrib/3.5/dplyr_0.7.6.tgz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 5686536 bytes (5.4 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 5.4 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/macosx/el-capitan/contrib/3.5/ggplot2_3.0.0.tgz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 3577658 bytes (3.4 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 3.4 MB
When the installation is complete, you will see a status message like:
The downloaded binary packages are in
/var/folders/7g/r8_n81y534z0vy5hxc6dx1t00000gn/T//RtmpJECKXM/downloaded_packages
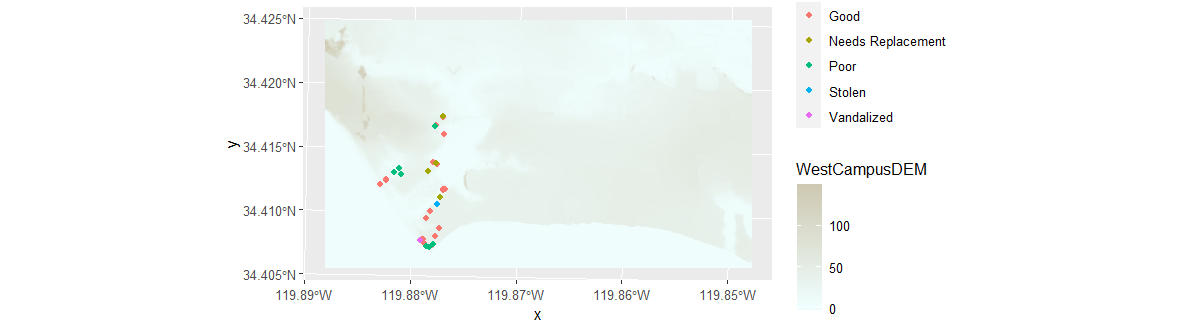
Make the test map
If you do not know how to run R scripts, you may want to consider taking our Intro to R in the Fall!
-
Download and install
InstallTest.zipfrom our Google Drive. -
Launch RStudio by double-clicking
InstallTest.r -
The following image should draw (you may need to click “Zoom” to get this format
You are now ready for the workshop!
We maintain a list of common issues that occur during installation as a reference for instructors that may be useful on the Configuration Problems and Solutions wiki page.